Inferring the MoA of drugs based on barcode fingerprints
Welcome
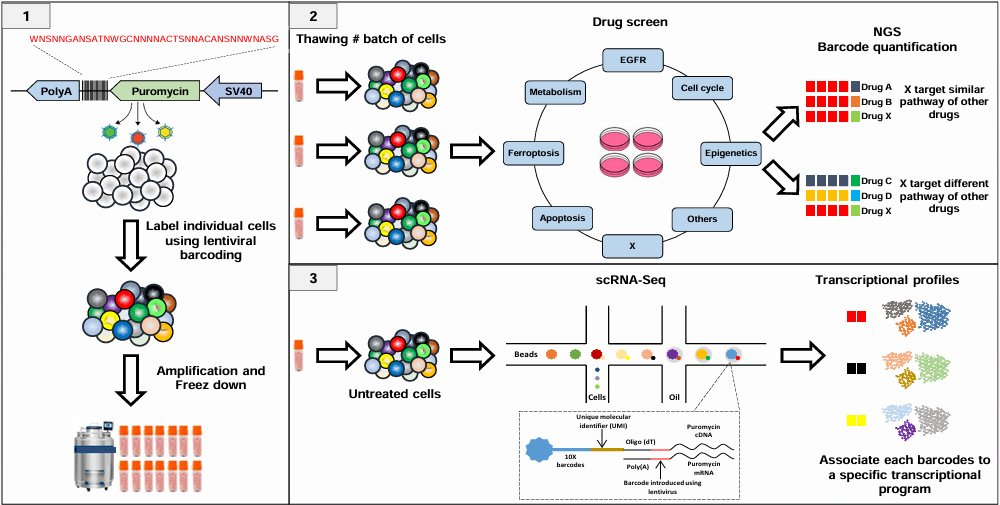
This is the online Quarto book project for reproducing: Inferring the mechanism of action of new drugs through the analysis of the predetermined heterogeneous response to treatment of different subpopulations of cancer cells poster, presented at NetBioMed 2022 conference.
Introduction: Cell lines DNA Barcoding
DNA barcoding is also used for inferring the species abundances in environment samples, just replace the notion of species by cell lines. Similar statistical issues, with zero-inflated distributions.
Steps:
- Transfection by virus.
- Clonal amplification, unique tagging per cell using MOI.
- Clone sizes are assumed to be proportional to the barcode abundances due to this 1-1 mapping of a barcode and a single cell.
Pros DNA barcoding:
- Better capture of cell population sizes
- Better tracking of tagged clones.
Cons DNA barcoding:
- Lack of systematic reviews and benchmarks.
- Mostly rely on bulk RNASeq analytical tools, not accounting for drop-outs. In particular, the assumptions that variance across tags is homogeneous, and abundances follow a negative binomial distribution are quite controversial.